list-watch 是一种用于监视和处理资源变化的机制,广泛应用于分布式系统和微服务架构中,尤其是在 etcd 和 Kubernetes 中。
在 Kubernetes kube-apiserver 处于最核心的位置。所有组件(kubelet、scheduler、controller-manager)和 Kubernetes 集群的交互都需要经过 kube-apiserver。当集群中的各节点或模块需要获取或操作数据时,都需要通过 kube-apiserver 提供的 RestFul 接口进行增删改查。
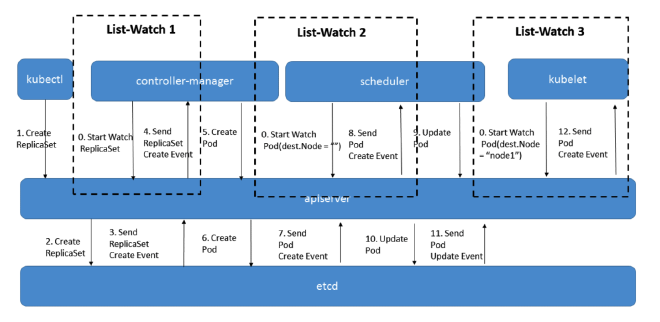
上图是一个 Pod 从创建到运行的流程。List&watch 是 k8s 统一的异步消息处理机制,list 通过调用资源的 list API 罗列资源,基于 HTTP 短链接实现;watch 则是调用资源的watch API 监听资源变更事件,基于 HTTP 长链接实现。在 k8s 中,各组件通过监听 Apiserver 的资源变化,来更新资源状态。
需要强调的是,List&Watch 的数据都是来自于 ETCD 的数据,ETCD 中存储了集群的所有数据。Apiserver 的主要任务就是获取最新的 etcd 数据并返回给 client。
当 kube-apiserver 监听到各组件发来的 watch 请求时,由于 list 和 watch 请求的格式相似,先进入 ListResource 函数进行分析,若解析为 watch 请求,便会创建一个 watcher 结构来响应请求。watcher 的生命周期是每个 http 请求的。kube-apiserver 从 ETCD 读到的数据存在 cacher 中。 cacher 也是 Storage 类型,这里 cacher 可以理解为是监听 etcd 的一个实例,cacher 针对于某个类型的数据,其 cacher 通过 ListAndWatch() 这个方法,向 etcd 发送 watch 请求。etcd 会将某一类型的数据同步到 watchCache 这个结构,也就是说,ListAndWatch() 将远端数据源源不断同步到 cacher 结构中来。
type watchCache struct {
sync.RWMutex //同步锁
cond *sync.Cond //条件变量
capacity int //历史滑动窗口容量
keyFunc func(runtime.Object) (string, error) //从storage中获取键值
getAttrsFunc func(runtime.Object) (labels.Set, fields.Set, bool, error) //获取一个对象的field和label信息
cache []watchCacheElement //循环队列缓存
startIndex int //循环队列的起始下标
endIndex int //循环队列的结束下标
store cache.Store//
resourceVersion uint64
onReplace func()
onEvent func(*watchCacheEvent) //在每次缓存中的数据发生 Add/Update/Delete后都会调用该函数,来获取对象的之前版本的值
clock clock.Clock
versioner storage.Versioner
}
Informer #
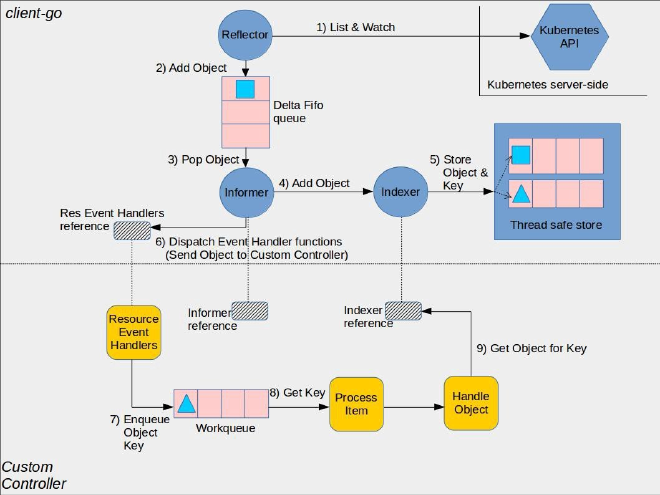
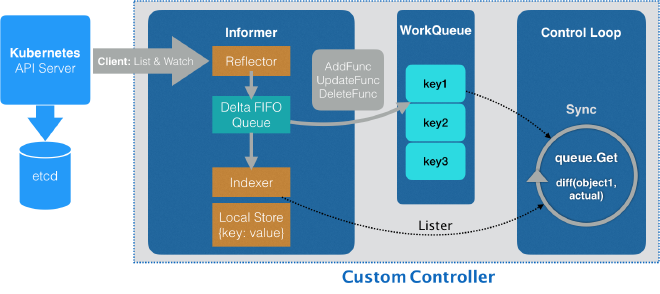
client-go 库中定义了 List&Watch 的客户端请求和机制,上图就是其中各个组件的工作原理及其与开发自定义控制器代码的交互点。其中
- Reflector:用于监控 Kubernetes 资源变化,其功能由
ListAndWatch函数实现。当 Reflector 接收到资源变更的事件,会获取到变更的对象并在函数 watchHandler 中放到 DeltaFIFO 队列。 - DeltaFIFO:是一个 FIFO 的队列,用来缓存 Reflector 拉取到的变更事件和资源对象。
- Informor:是流程中最重要的节点,是整个流程的桥梁。其功能在 processLoop 函数中实现,负责:
- 从 DeltaFIFO 中 pop 出对象并更新到 Indexer 的 cache 中;
- 调用自定义 Controller,传递该对象。
- Indexer 在资源对象上提供了索引和本地缓存的功能。经典的使用场景是基于对象的
Labels创建索引,Indexer 可以支持使用索引函数来维护索引,同时 Indexer 使用线程安全的DataStore来存储资源对象和对应的 Key。
Indexer #
默认使用的是 cache 包里的 MetaNamespaceKeyFunc 函数来生成对象的Key,格式如:
当创建资源的Informer,对应资源的全量数据都会缓存在对应的 Indexer 中并通过Reflector监听变更同步更新。client-go查询时就可以优先查询本地缓存,降低Kubernetes APIServer和ETCD的压力。(可以认为 Indexer 中包含 ETCD 的全量数据)
源码 #
定义
NewIndexer 方法
// NewIndexer returns an Indexer implemented simply with a map and a lock.
func NewIndexer(keyFunc KeyFunc, indexers Indexers) Indexer {
return &cache{
cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(indexers, Indices{}), // 线程安全
keyFunc: keyFunc, // 用于后续存储对象时生成map的key,通常为格式为:namespace/name
}
}
Cache 定义
// `*cache` implements Indexer in terms of a ThreadSafeStore and an
// associated KeyFunc.
type cache struct {
// cacheStorage bears the burden of thread safety for the cache
cacheStorage ThreadSafeStore
// keyFunc is used to make the key for objects stored in and retrieved from items, and
// should be deterministic.
keyFunc KeyFunc
}
// IndexFunc knows how to compute the set of indexed values for an object.
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
// Indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
KeyFunc 定义
// KeyFunc knows how to make a key from an object. Implementations should be deterministic.
type KeyFunc func(obj interface{}) (string, error)
// MetaNamespaceKeyFunc is a convenient default KeyFunc which knows how to make
// keys for API objects which implement meta.Interface.
// The key uses the format <namespace>/<name> unless <namespace> is empty, then
// it's just <name>.
func MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj interface{}) (string, error) {
if key, ok := obj.(ExplicitKey); ok {
return string(key), nil
}
objName, err := ObjectToName(obj)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return objName.String(), nil
}
func (objName ObjectName) String() string {
if len(objName.Namespace) > 0 {
return objName.Namespace + "/" + objName.Name
}
return objName.Name
}
NewThreadSafeStore 方法
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indices maps a name to an Index
type Indices map[string]Index
// NewThreadSafeStore creates a new instance of ThreadSafeStore.
func NewThreadSafeStore(indexers Indexers, indices Indices) ThreadSafeStore {
return &threadSafeMap{
items: map[string]interface{}{}, // 对于存储具体对象,是一个线程安全的map。
index: &storeIndex{
indexers: indexers, // 是一个map,存放生成索引的函数,NewIndexer传递进来的。
indices: indices, // 是一个map, 存放生成的索引数据,传递进来的是Indices{}空对象。
},
}
}
threadSafeMap 定义
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex // 读写锁
items map[string]interface{} // 用于存储缓存的数据,key -> 资源对象
// index implements the indexing functionality
index *storeIndex // 用于存储 1.生成索引的函数 2.根据索引函数生成的索引数据
}
storeIndex 定义
// storeIndex implements the indexing functionality for Store interface
type storeIndex struct {
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers // 实际上是 map[string]IndexFunc
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices // 实际上是 map[string]Index
}
// IndexFunc knows how to compute the set of indexed values for an object.
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
// Indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Index maps the indexed value to a set of keys in the store that match on that value
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indices maps a name to an Index
type Indices map[string]Index
Reflector #
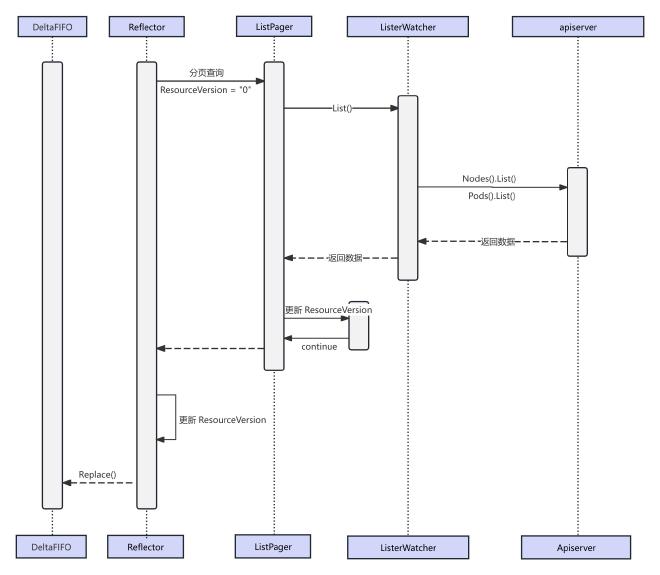
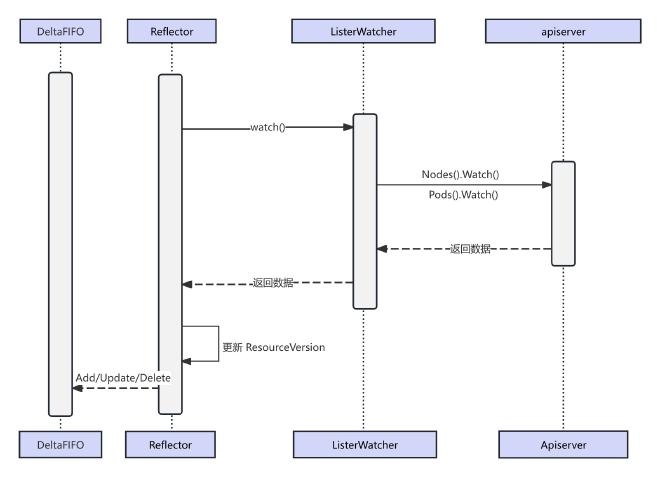
Reflector 基于 List&Watch 机制监控 Kubernetes 资源变化,当 Reflector 接收到资源变更的事件,会获取到变更的对象并放到 DeltaFIFO (先进先出)队列。
Reflector 的核心逻辑在 ListAndWatch 函数中:进行 List 拉取全量数据,初始化 Delta FIFO 数据;Watch 监控资源变更;启动 Resync 机制
数据结构:
// client-go/tools/cache/reflector.go
type Reflector struct {
// name identifies this reflector. By default it will be a file:line if possible.
name string
// reflector 对象需要监控的资源类型,比如 &v1.Pod{}, &v1.Deployment{}
expectedType reflect.Type
// deltaFIFO 队列存储对象
store Store
// 实现 list/watch
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// 拉取全量数据时,为避免给服务器造成太大压力,首先使用的是分页方式分片拉取。
WatchListPageSize int64
// 上次更新的资源版本号,用来判断当前的node的资源状况
lastSyncResourceVersion string
......
}
DeltaFIFO #
DeltaFIFO 是一个缓冲先入先出队列,用于保存从 Relfector 中获取到的数据,即相应的操作数据对象,最终会被 Informer 消费。Delta 即抽象出来的 Kubernetes 中对象的变化,比如 Pods 或 Nodes 的增删改查。相应的 Delta 定义和类型如下
// client-go/tools/cache/delta_fifo.go
type DeltaType string // Delta类型
const (
Added DeltaType = "Added" // 增加
Updated DeltaType = "Updated" // 更新
Deleted DeltaType = "Deleted" // 删除
Sync DeltaType = "Sync" // 同步
)
type Delta struct {
Type DeltaType // Delta类型
Object interface{} // 对象,Delta的粒度是一个对象,例如POD对象,Service对象等
}
type Deltas []Delta // Delta列表
数据结构
// client-go/tools/cache/delta_fifo.go
type DeltaFIFO struct {
lock sync.RWMutex // 读写锁,在多读少写的场景下性能优势明显。
// 条件变量,用于实现多协程之间基于条件的同步机制。
// 它允许一个或多个协程等待特定条件的满足,并且在条件满足时能够被唤醒。
// sync.Cond.Wait()休眠 sync.Cond.Broadcast()唤醒
cond sync.Cond
items map[string]Deltas // 按照 kv 的方式存储对象,但是存储的是对象的 Deltas 数组
queue []string // 这个是为先入先出实现的,存储的就是对象的键
keyFunc KeyFunc // 对象键计算函数,默认使用 MetaNamespaceKeyFunc
...
}
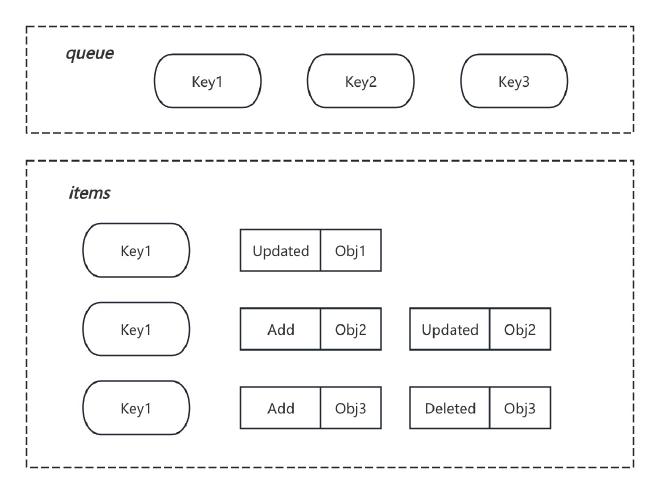
其中用于存储的主要为以下两个字段,对应的存储结构如图
queue字段存储资源的 key,由KeyOf函数 (MetaNamespaceKeyFunc) 计算得到;items字段存储的 Deltas 数组,是具体的资源事件内容。
Add #
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Add(obj interface{}) error {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
f.populated = true
return f.queueActionLocked(Added, obj)
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionLocked(actionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {
return f.queueActionInternalLocked(actionType, actionType, obj)
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionInternalLocked(actionType, internalActionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj) // 使用 MetaNamespaceKeyFunc 计算 key: namespacexx/podxx
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
...
oldDeltas := f.items[id] // 通过 Key 获取已存在的 Deltas 列表
newDeltas := append(oldDeltas, Delta{actionType, obj}) // 添加到 Deltas 列表中
newDeltas = dedupDeltas(newDeltas) // 相邻事件去重
if len(newDeltas) > 0 {
if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {
f.queue = append(f.queue, id) // 将 MetaNamespaceKeyFunc 计算 key 放到列表尾部
}
f.items[id] = newDeltas // 将更新后的 Deltas 列表重新放入 map 中
f.cond.Broadcast() // 广播唤醒所有调用 sync.Cond.Wait() 休眠的 goroutine.
}
...
}
Pop #
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
for {
for len(f.queue) == 0 {
...
f.cond.Wait() // 如果队列为空,则休眠,等待 sync.Cond.Broadcast() 唤醒
}
// 从 queue 取出第一个元素,然后覆盖第一个元素(FIFO 的核心原理)
id := f.queue[0]
f.queue = f.queue[1:]
// 在 go 中,queue[1:] 这样的操作是非常高效的,它并不会直接复制数组,而是创建一个新的切片结构,指向原数组的子集
// 根据 MetaNamespaceKeyFunc 生成的 key 获取具体 Delta 列表
item, ok := f.items[id]
if !ok {
// This should never happen
klog.Errorf("Inconceivable! %q was in f.queue but not f.items; ignoring.", id)
continue
}
...
// Don't need to copyDeltas here, because we're transferring
// ownership to the caller.
return item, err
}
}
Informer #
Informer 可以理解成是 Kubernetes client-go 提供的一种本地缓存机制,以减轻 kube-apiserver 的访问压力。由于 kube-apiserver 是整个集群的中心,集群控制的入口,所有模块对集群的操作都需要经过其提供的 RestFul 接口,大量组件对 apiserver 以及 ETCD 的访问会造成非常大的压力。
Lister() 方法, List/Get Kubernetes 中的 Object 时,Informer 直接查找缓存在本地内存中的数据(这份数据由 Indexer 维护),而不是去请求 Kubernetes API。这样,Informer 既可以更快地返回结果,又能减少对 Kubernetes API的直接调用。
Informer 缓存机制实现主要为以下几点:
- Informer 会在本地缓存一份较实时的 Kubernetes 资源数据,可以直接进行本地查询。
- 如果资源发生变化,通过 Watch 长连接机制,推送至本地 Informer 并更新本地缓存。
- 缓存发生变更会,会触发本地处理函数执行相关业务逻辑
Informer 只会调用 Kubernetes List 和 Watch 两种类型的API。在其初始化时,首先调用 List 获取对应资源的所有对象,存在本地缓存中;随后调用 Watch 获取长连接来监视资源的变化,不再调取其他接口。
Informer 和 kube-apiserver 之间没有 resync 机制(实现中的 resync 其实也只是将本地缓存的数据再构造成事件再次同步到队列一次),因为能保证 list+watch 不会丢失事件,如果网络抖动重新恢复后,watch 会带着之前的 resourceVersion 号(单调递增)重连,apiserver 收到该请求后会将所有大于该 resourceVersion 的变更同步过来。
Informer 可以添加自定义的回调函数,这个回调函数实例(即 ResourceEventHandler 实例)只需实现 OnAdd(obj interface{}) OnUpdate(oldObj, newObj interface{}) 和 OnDelete(obj interface{}) 三个方法,分别对应了 Informer 监听到创建、更新和删除这三种事件类型。
Informer 的底层缓存机制中使用了二级缓存,分别为 DeltaFIFO 和 LocalStore。
- DeltaFIFO 用来存储 Watch API 返回的各种事件
- LocalStore 只会被 Lister 的 List/Get 方法访问
虽然 informer 没有 resync 机制,但 Informer 内部的这两级缓存之间存在 resync 机制。具体相关讨论详见链接。
问题 #
List-Watch 怎样保证事件不丢失 #
- Kubernetes 有一个 ResourceVersion 的概念,表示资源的版本号。当 List 的时候会获取当前资源的 ResourceVerison,之后再 Watch 的时候传入这个 ResourceVersion,kube-apiserver 会将这个 ResourceVersion 之后的变更推送给 Client。
- Watch 断开重连时,会使用最近的 ResourceVersion 尝试重新建立连接。
- 如果 Client 侧请求的 ResourceVersion 在 ETCD 中不存在时,kube-apiserver 会返回
KubernetesTooOldResourceVersionException要求 Client 重新进行 List-Watch 更新 ResourceVersion
